Development of EAF Smelting Plain Carbon Steel

Development of EAF Smelting Plain Carbon Steel
At present, the mainstream steelmaking processes are converter steelmaking process and electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking process. EAF steelmaking process has small pollutant emission, flexible organization, many varieties, and its output accounts for 27% of the world's steel output, while China's current EAF steelmaking output is only 10% of the total steel output. UHP graphite electrode as the electric conductor meets the requirments of overall EAF steelmaking. In 2019, China's steel production reached 996 million tons, accounting for 53% of the world's steel production. The development of EAFs can reduce carbon emissions, greenhouse gas emissions and protect the earth's environment.
Electric arc furnace short process is a kind of steelmaking process using social scrap steel to achieve circular economy. The pollutant emission of the whole scrap smelting process is only 20% of that of the long process of the blast furnace converter. The advantages of blast furnace converter steelmaking process are: large output, low cost per ton of steel. At present, the cost of converter steel is 400~500 yuan lower than that of electric furnace steel; Its disadvantage is serious environmental pollution. From 2016 to early 2018, when the converter production cost is higher than EAF production cost, EAF smelting of general carbon steel has advantages. When EAF steelmaking production cost is low and the country has strict environmental protection requirements, steel enterprises will give priority to the use of EAF steelmaking process.
1. Brief introduction to development of EAF steelmaking
The maturity period of traditional EAF steelmaking is from 1945 to 1982 when LF furnace was introduced. The traditional EAF steelmaking technology is a process mainly involving melting period, oxidation period and reduction period, mainly producing special steel. After 1980, continuous casting gradually replaced mold casting, ultra-high power EAF and oxygen technology for EAF appeared, and the modern EAF steelmaking stage began. The EAF steelmaking process can not only produce special steel, but also general carbon steel (plain carbon steel is the representative steel, including long and flat products, the carbon content is 0.06~0.38%, and the phosphorus and sulfur content is 0.035~0.050%). For example, in the Middle East and North America, plain carbon steel is mainly produced by EAF short process. The modern EAF steelmaking technology regards the EAF as a primary smelting furnace, and the reduction period of the EAF is completed by LF and other external refining equipment. The oxygen blowing process is added to realize the input of chemical energy. Short process smelting, mainly with EAF equipment, is a process to refine scrap based ferrous raw materials into final steel by EAF, LF furnace, continuous casting machine, long rolling mill or flat rolling mill. The converter steelmaking is provided with molten iron by the blast furnace, the raw materials of the blast furnace are iron containing raw materials such as sintering and pellets, and the coke is provided by the coke oven, so the converter blast furnace process is also called the long process. The short process EAF production has the following characteristics: the smelting cycle of continuous casting and EAF is 40~50min, fast pace; Hot charging or casting rolling endless rolling only takes 2-3 hours from scrap to finished product. EAF steelmaking, especially the short process bar, wire and long material production lines for producing plain carbon steel, are all over the world to meet the needs of local economy and society.
There is a big difference in carbon dioxide emission between converter and EAF steelmaking process. Long process blast furnace converter needs to reduce iron ore to iron, and smelting 1t steel needs to emit 2200kg CO2; The the short process EAF melts the scrap steel, and then deoxidizes and alloys it. There is no process of large-scale reduction of iron oxide, so the carbon dioxide emission is greatly reduced. Smelting 1t steel will emit 120kg CO2, as shown in Figure 1. Therefore, the EAF steelmaking process is more environmentally friendly than the blast furnace converter process.
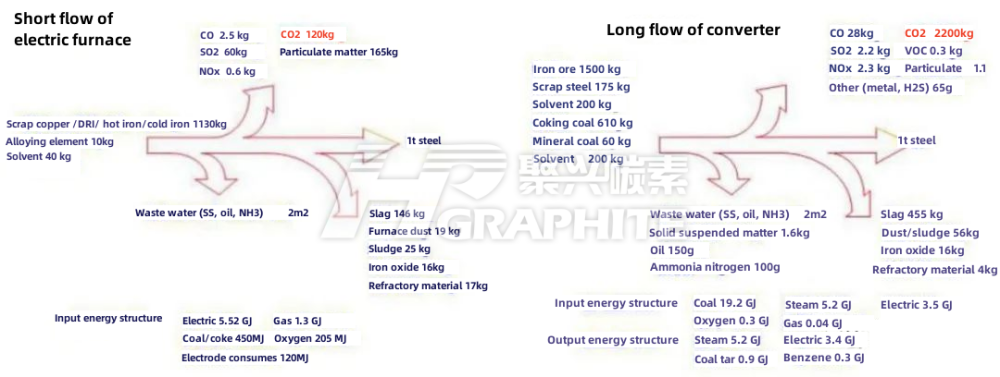
Figure 1: Energy balance and material balance of EAF short process and blast furnace converter long process
According to the data of the World Steel Association, as shown in Table 1, the proportion of EAF steel in countries such as the United States and India has increased from 2006 to 2019, the proportion of EAF steel in South Korea has decreased, while the proportion of EAF steel in Germany and Japan has not changed much. However, the proportion of EAF steel in Japan, the United States, South Korea, Germany and other developed countries is higher than that in China. Developed countries develop to a certain stage, the social accumulation of steel scrap increase. The scrap is recycled through the EAF steelmaking process. The development path of steel industry in developed countries provides ideas and experience for optimizing the process structure of China's steel industry, which can reduce pollution emission, protect the environment, and realize green steelmaking and intelligent manufacturing by optimizing the process structure of China's steel industry through electric furnace steelmaking process. It is estimated that in 2030, China's annual social steel scrap accumulation will reach 320 million to 350 million tons, and in 2035, China's annual social steel scrap accumulation will reach 446 million tons. The electric furnace scrap resources are sufficient, which will lay a foundation for the development of EAF steelmaking in China. For the current EAF steelmaking dynamics, welcome to consult us.
Table 1 Proportion of EAF steel in major steel producing countries in the world
Year | World | Japan | America | Korea | Germany | India | China |
2006 Y | 32.0 | 26.0 | 56.9 | 45.7 | 31.1 | 50.5 | 10.5 |
2019 Y | 27.7 | 24.5 | 69.7 | 31.8 | 30.0 | 56.2 | 10.4 |
No related results found








0 Replies