【Steel】Prices Surge Nearly 220! Mill Profits Hit 300 RMB/Ton – Where Is the Market Heading?

Graphite electrodes are vital to EAF steelmaking—acting as the "core component" for arc heating. With excellent conductivity and heat resistance, they're key to improving steel quality and output. Master them, master EAF steelmaking!
【Steel】Prices Surge Nearly 220! Mill Profits Hit 300 RMB/Ton – Where Is the Market Heading?
Tariff Storm vs. Domestic Demand: Steel Industry at a Crossroads
Trump's tariff policies are sweeping through the global economy like a storm. According to the UNCTAD, these policies have driven up global supply chain costs and disrupted supplies, with the least developed countries being hit the hardest. The U.S. Federal Reserve's Beige Book also shows rising costs being passed to end-users, and the ripple effects across the global trade system are deeply impacting the steel sector.
Domestically, under a series of macro policies led by regulators, industries such as steel, coal, photovoltaics, and automobiles have begun to "reverse involution," pushing transformation from low-end to high-quality development. Since June, the coking coal market has led the uptrend, with futures rising from 709 RMB/ton to a high of 928 RMB/ton — an increase of 218 RMB/ton. So, what's next for steel prices?
1. Global Steel Landscape Under Tariff Shadows
U.S. tariff policies are reshaping global steel trade. According to WTO data, global merchandise trade volume is expected to drop by 0.2% in 2025, with North America's exports falling 12.6%. For steel, this shock is twofold: domestic U.S. steel import costs surge, lifting local prices, while exporting countries—especially developing economies—face order losses, idle capacities, and shrinking forex income, putting fragile economies under immense pressure.
China, as a major steel producer and consumer, has partly absorbed the shock due to its industrial scale. From January to June, China exported 58.147 million tons of steel, up 9.2% year-on-year. While exports appear strong, billet exports—less affected by tariffs as they are rolled into finished products abroad—have hit record highs, reflecting concerns over deteriorating global trade conditions.
As the U.S. raises tariff barriers, steel flows previously destined for North America are being diverted elsewhere, causing regional supply-demand imbalances and adding uncertainty to domestic steel prices.
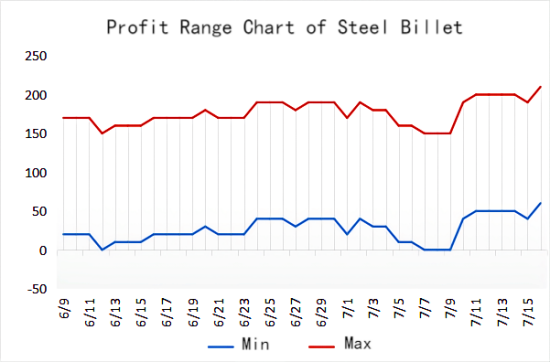
2. Domestic Demand Restructuring in Steel
Steel demand in China is undergoing profound restructuring. Despite better-than-expected GDP growth in H1, the "strong supply, weak demand" pattern persists. In real estate, the "intensive" development path set during the national urban work meeting signals the end of large-scale expansion, structurally shrinking demand for construction steel like rebar.
Stats show that while excavator output grew 12.4% YoY in H1, small tractor output fell 15.8%, revealing divergence in infrastructure and agricultural machinery demand.
The home appliance sector also shows a mixed picture: washing machine output rose 10.3%, supporting cold-rolled coil demand, while TV output dropped 5.5%, dragging down coated sheet consumption.
This divergence reflects the structural nature of steel demand: traditional sectors are shrinking while emerging ones grow, but the total momentum for expansion remains weak.
Although nine major international investment banks have revised China's GDP forecast upward to nearly 5%, achieving this will require sustained improvements in real estate, consumption, and exports — making an explosive rebound in steel demand unlikely in the short term.
Meanwhile, blast furnace profits are recovering, with wire rod profits reaching 300 RMB/ton and billet at 175–200 RMB/ton. Mills are adjusting production pace, creating a "spec shortage" illusion in the market.
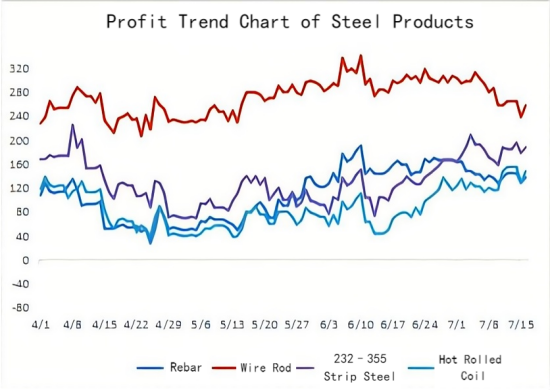
3. Market Tug-of-War: Price Fluctuations & Policy Hopes
The steel market is now locked in a tug-of-war. Iron ore prices stay strong due to high hot metal output and blast furnace utilization, but the $100 resistance level remains. If coking coal and coke continue to rebound, they'll provide cost support for steel prices; if not, the profit recovery may again be squeezed.
Market sentiment shows caution: seasonal demand has entered a lull, weakening spot liquidity. Yet, reduced deliveries from construction steel mills and low trader inventories have strengthened price-holding sentiment, limiting downside.
July's rebound, driven by policy signals, ended a five-month slump. But sustaining the uptrend requires improved macro expectations. H1 GDP reached 66 trillion RMB, still far from the full-year target of 140 trillion. Growth-supportive policies are expected in H2 — a key variable for any breakout in steel prices.
With global trade friction and domestic structural change at play, the steel sector is in deep transition.
Short term: Policy stimulus and peak season demand may offer opportunities for a price rise.
Long term: Demand structure will be reshaped by real estate transformation and manufacturing upgrades, with risks peaking around mid-September.
For market participants, it is crucial to monitor both raw materials (iron ore, coking coal) and the effects of real estate policies, consumption recovery, and export performance — the interplay of these variables will determine the steel industry's next direction.
For more insights on the steel sector, contact an analyst anytime and seize the opportunity to buy low and sell high.
Feel free to contact us anytime for more information about the EAF Steel market. Our team is dedicated to providing you with in-depth insights and customized assistance based on your needs. Whether you have questions about product specifications, market trends, or pricing, we are here to help.
No related results found








0 Replies