Two-Step Needle Coking Process

Overview
Lummus Technologies has been developing and designing coking technology as early as the mid 1930s. In 1938, Lummus designed and built the first delayed coking unit for Gulf Oil company, to get the graphite electrode products containing Needle Coke. Since the 1960s, Lummus has also carried out and completed a number of R & D and engineering projects aimed at producing high-quality needle coke.
In 1960s, the company licensed, designed and built three sets of devices for producing high-quality anode coke and needle coke in Japan, of which the first set was put into commercial operation in 1967:
Sino Coal Chemical Co., LTD. (Nippon Tetsukino Chemical co., LTD.) - 1966
MITSUBISHI - 1969
Sino Coal Chemical Corporation (Nippon Tetsukuno Chemical) - 1973
Japan Steel Tube Company - 1985
In 1978, Lummus provided baosteel of China with a set of technology license and process package of coal-based anode coke production device through Japan Iron and Steel Corporation. Subsequently, Baosteel also carried out the research and development of needle coke.
In 1980, Lummus licensed and designed a needle coke device from Highball, using most advanced and proprietary two-step coking technology of Lummus at that time.
In 2011, South Korea OCI company and POSCO/Mitsubishi Chemical (PMC) successively adopted rums coking production process to produce needle coke, among which PMC produces high-quality needle coke for its parent company Posco chemical factory to produce anode materials.
In 2013, CLG obtained exclusive licensing rights to Lummus needle coke technology. In 2018, a famous refining and chemical group in Shandong finally selected CLG's most advanced two-step coking process to produce high-quality needle coke after careful investigation and investigation, combined with pilot test verification.
Introduction of two-step coking process
Carbonization temperature can greatly affect the quality of needle coke, especially the coefficient of thermal expansion CTE. The characteristics of raw materials usually determine the optimum carbonization temperature, which ensures that the resulting coke exhibits excellent needle-like structure and a low coefficient of thermal expansion.
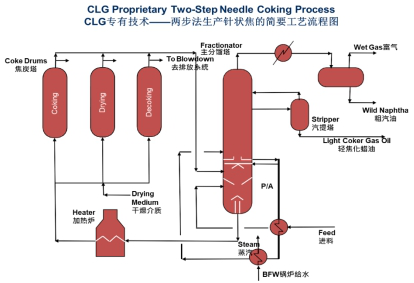
The CLG two-step coking technology can ensure that the first stage of coking can be carried out at a lower temperature, which reduces the reaction rate and increases the reaction time, which is conducive to the formation and polymerization of mesophase. This operating condition can also ensure a lower coefficient of thermal expansion of coke products after calcination and graphitization. In the second stage, a higher temperature is used to complete the coking reaction, reducing the content of combustible volatile VCM and increasing the strength of coke products.
In conclusion, the two-step needle coking technique allows the reaction rate to be controlled and the mesophase to be fully grown and polymerized before the interlayer links between different carbonized layers are established. However, in the traditional coking design, the coking reaction can not be controlled step by step, which hinders the gradual generation of mesophase and the orderly establishment of the cross-layer link, and finally makes the crystallinity of coking higher, for more technical news contact us here.
No related results found








0 Replies